
Artificial intelligence (AI) is coming! Although a lot of work will be replaced, there are still many tasks - including some work on assembly lines - that are still too complicated for machines. In addition, ethical issues also trouble us.
This is a topic of concern at the 18th annual EmTech Conference held at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The focus of the conference was on AI and robotics, and participants were eager to discuss the great progress of AI in changing the way of our life and work.
Ethical issues are not only resulted from technologies such as AI, but also from the rise of the Internet, mobile phones and social media. Gideon Lichfield, editor-in-chief of the MIT Technology Review, openedthe discussion with technical ethics. He showed a tweet-based image representing the political polarization.
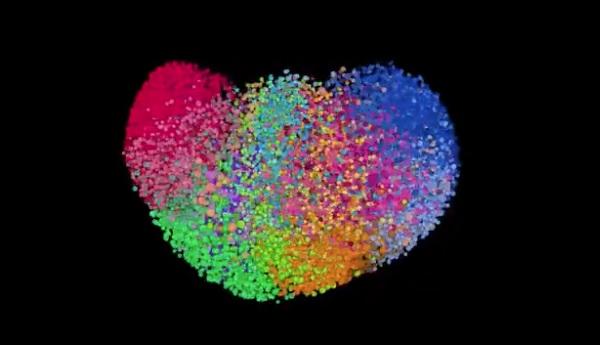
The EmTech MIT 2018 conference presented a picture of an analysis of tweets,showing the polarization of politics (Source: MIT Technology Review)
Lichfield said: " We will tend to flock with like-minded people. We will filter out tweets or information that are not in line with our position." He said that people believe that information can save politics, and if you don't like the content displayed, you will simply try to smash the data. The cover of the 2013 MIT Technology Review had a quote: The mobile phone, the Net, and spread of information - a deadly combination for The dictators, whichsounds even more practical now.

In 2013, people believed that big data could save politics... (Source: MIT Technology Review)
Lichfield went on to point out that Silicon Valley held that we are only creating technology and being neutral. But this is not the case. Why? Because you can't predict how people will use these technologies. For example, software can be used to change your expression in the video or to make you change to the extent before being passed on to others. Will Knight, editor of the MIT Technology Review, demonstrated how to replace the actor Paul Rudd with Ted Cruz in a video viaa free software. "The mere creation of technology is no longer feasible. We need to standardize these technologies for society."
MIT professor Josh Tenenbaum pointed out that AI has the potential to change society, but it still has a long way to go. His research team is now looking for ways to make machines learn in a way that simulates human learning.
"How come thatnow we have all the AI algorithms, but can't realize the real AI?" he asked. According toTenenbaum, the machine still lacks the learning ability and human knowledge. "The algorithm is not comparable to a first-grader." So far, the machines used nowadays, especially the machines in the factories, can only do one thing - such as welding - perhaps they can do more accurately than human beings, but that’s all the robots can do.Tenenbaum wants to understand why humans can do more than machines. "Modern AI technologies are driven by pattern recognition and deep learning. Wisdom is even more so."

MIT Professor Josh Tenenbaum explains how cognitive science has evolved into AI (Source: Martin Rowe)
Tenenbaum and his students are trying to reverse engineer the way people think and solve problems and then apply them to machines. He reported some exciting progresses and said that although deep learning mathematics was published in psychology journals from the 1960s to the 1980s, we still have a long way to go.
Tenenbaum also noted the famous paper published by Alan Turing in 1950, which mentioned that the only way to know how wisdom is developed is through children. Turing holds that child's brain is like a blank sheet of paper, but Tenenbaum believes it otherwise. For example, Professor Rebecca Saxe pointed out that we are born with the ability to engage in wisdom and learning. "We understand people, places and things, not just patterns and pixels." Professor Laura Schulz studies how children learn through thinking. Tenenbaum expects their research to simulate how we learn and apply it to machines.
Tenenbaum went on to show two films about children's problem solving, which the current machines can't do. In one of the films, the children can stack the toy rings in order of size. Another film shows an adult who wants to put the books in a bookcase with a closed door, a child may know his needs and open the door for him.
Another speech by Clara Vu, co-founder and vice president of engineering at Veo Robot, echoes Tenenbaum's views. Vu explains that this is like the process involved with mascara, and modern machines are too complicated. However, Vu shows how industrial robots do the things that human can't do. She describes how robots are better at welding than humans do in a car factory, but the final assembly is still done by humans.Neither General Motors (GM) nor Tesla can automate the final assembly process because it involves many tasks and there are many different models.
Vu points out that the automation of a single process requires a team of engineers to work for months or years, which is a huge investment. If you need change anything during this process, you have to reprogram the machine. People are better at adapting, while "robots can't assemble cable harnesses. As manufacturers are required to launch a wide range of products, we need more flexible automation."
Clara Vu, co-founder and vice president of engineering of Veo Robot, points out that we need to have awareness and motivation to perform tasks (source: Martin Rowe)
"The very reason which makes industrial robots powerful is also the reason which makes them dangerous." Vu explains why robots must be placed behind the fence to ensure workers’ safety. Her company is developing algorithms that use sensors to detect the presence or proximity of workers near the robot. If someone is getting too close, the robot will stop working. "The system we built has fail-safe capabilities. First it analyzes the entire space. If there is no guarantee that the space will not be occupied, it will be considered as occupied." Although this function does not require machine learning, it does show how people can work with robots. Vu describes this as "old-fashioned artificial intelligence."
Vu explains that robotics includes drives. "Robots must perform tasks. Although the drive is simple, it's hard to perceive. We're still a few decades or centuries away from implementing machines driven by humans. There are numerous problems yet to be solved to build a flexible factory like humans, in which robots can also make cable harnesses."
Although both Tenenbaum and Vu believe robots are unable to compete with humans yet, Ganesh Bell, the Uptake founder claim that "Every company will restructure software. AI will process data collected from Internet of Things (IoT) devices. AI and forecasting analysis is the next step to improve productivity.” The software developed by Bell's company is used for predictive analytics. But he pointed out that humans still have to take action on these predictions to prevent unnecessary interruptions in machine operations.
Uptake founder Ganesh Bell says that AI will change the way people work, but people will still have to act according to AI's advice (Source: Martin Rowe)




















